Mitigating CVE-2024-3094
By now you’ve likely heard about the vulnerability in XZ Utils Data Compression Library that impacted multiple Linux distributions (CVE-2024-3094) and read the threat brief Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 posted.
I’m sure you understand all the recommended precautionary measures—downgrading vulnerable XZ Utils versions to 5.4.6 (the latest unaffected version), reverting affected Linux distributions to stable releases and treating any systems identified as vulnerable as potential security threats.
But where do you start?
Don’t panic. Take a deep breath. Let’s pause and take a minute to understand the impact of zero-day vulnerabilities before jumping into action. Remember what Benjamin Franklin said— “By failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail.”
The following list of questions allows you to plan for a vulnerability like CVE-2024-3094.
Understanding the Impact of Vulnerabilities: 5 Key Questions to Ask Yourself
When a new critical CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is discovered, it's easy to get caught up in the drama and feel like the sky is falling. But before you jump into action, it’s important to take a minute to understand the impact of the vulnerability so you can formulate an appropriate response.
Here are the top five questions you should ask yourself in such situations:
- Does this vulnerability affect me?
What assets are impacted by this vulnerability? Where are they running? Is this a production or non-production environment? - Am I at risk of attack?
Do you have assets at risk of exploitation? What are those? - Did this vulnerability lead to a compromise of my environment?
Do you know if the vulnerability has already been exploited by an attacker? Look for evidence of malicious activity and find any indicators of compromise. - Can I remediate the vulnerability?
Does it have a patch? What needs to be fixed? How is this vulnerability introduced into my environment? - What mitigation measures should we implement?
Can we apply a remediation strategy until the fix is applied, such as a policy to prevent new vulnerable deployments, or implement a control to detect and prevent attacks?
Asking these questions is the first step to assessing, prioritizing and mitigating the impact of critical CVEs—without losing your sanity.
How to Find and Fix CVEs in a Few Simple Clicks
More than 7,300 malicious OSS packages were discovered in 2022 across all major package manager registries according to the GitHub Advisory Database. With software supply chain attacks on the rise, finding and fixing zero-day vulnerabilities needs to be as simple as possible. Yet most security teams don’t have the tools they need—unless you count an array of complicated spreadsheets (and you shouldn’t).
Let's take a look at how easy it can be with Prisma Cloud, the Code-to-Cloud CNAPP…
Step 1: Identify running applications or workloads impacted by the vulnerability
For a specific vulnerability such as CVE-2024-3094, you can search your entire cloud estate, including both production and non-production workloads, and identify all the assets vulnerable to the CVE. With a Code to Cloud view into the comprehensive application lifecycle, it’s easy to trace the vulnerability to the repository where it’s stored and all the way back to the package where it originated from.
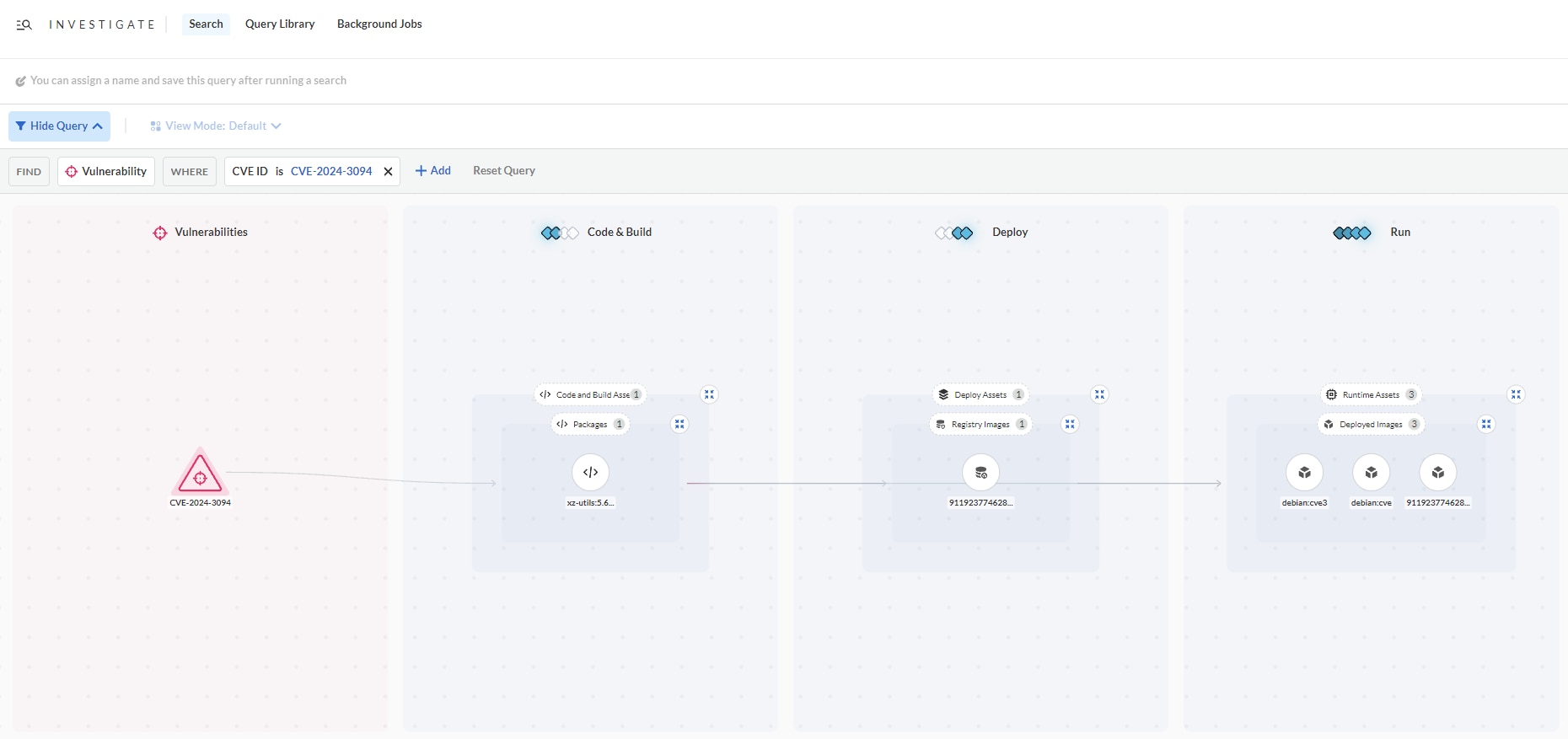
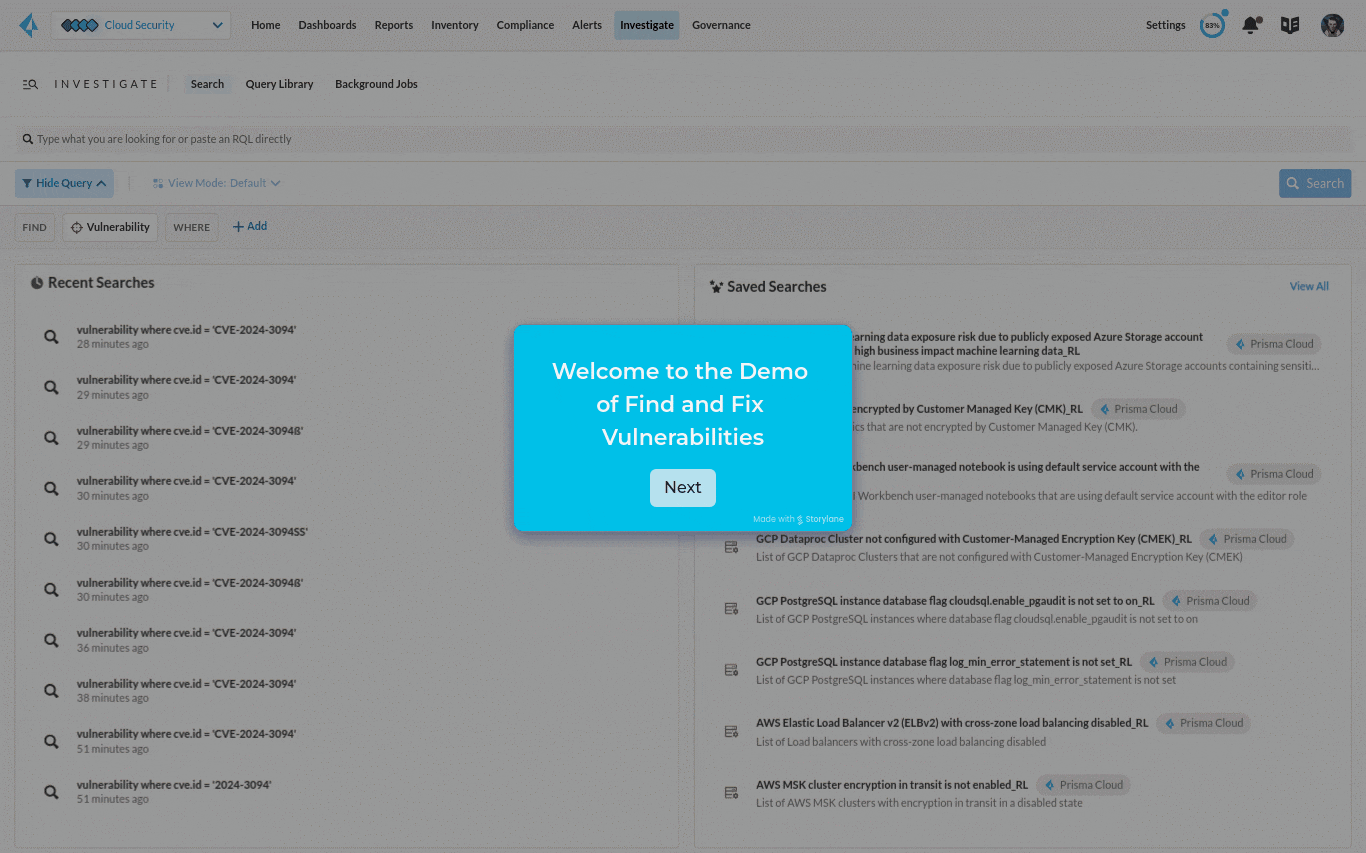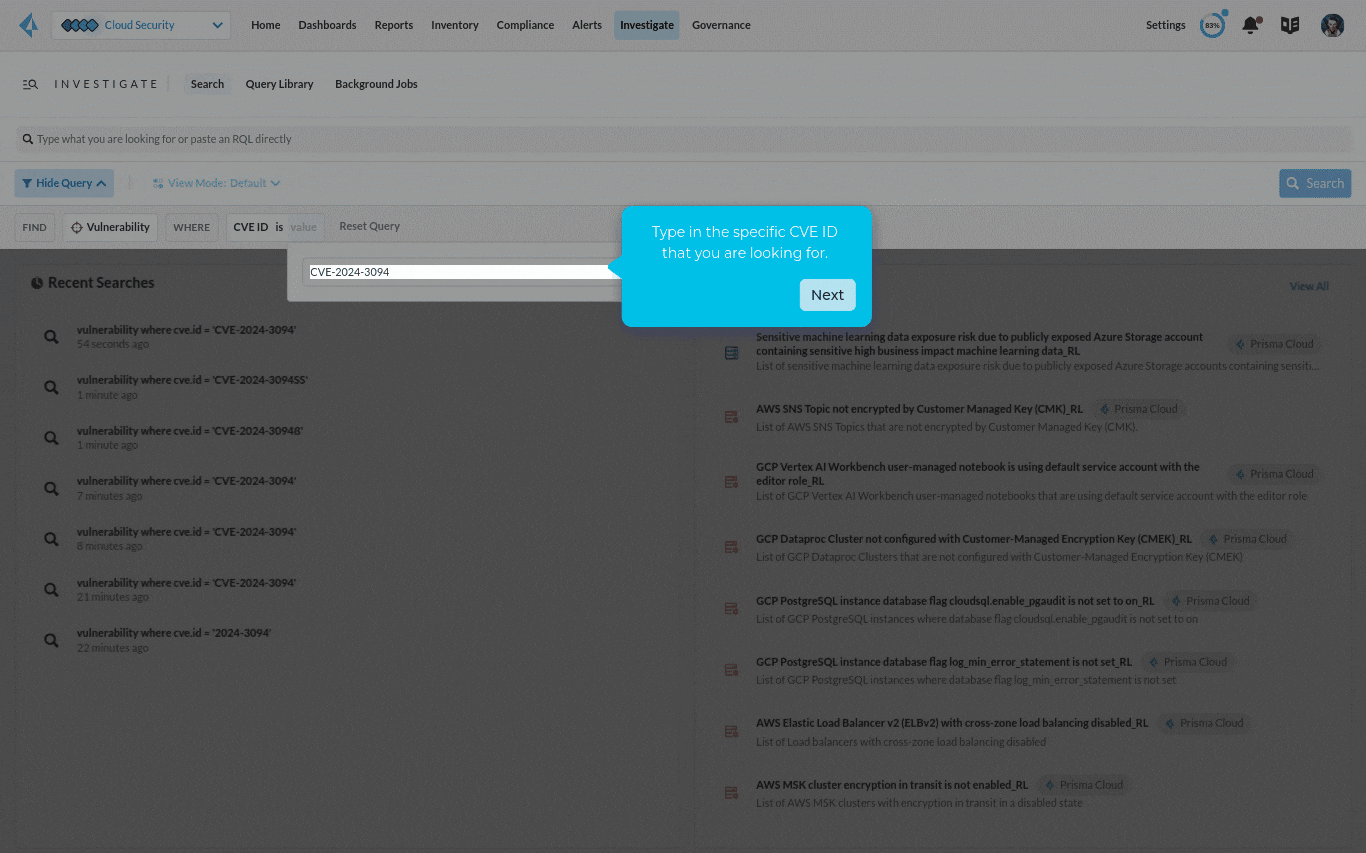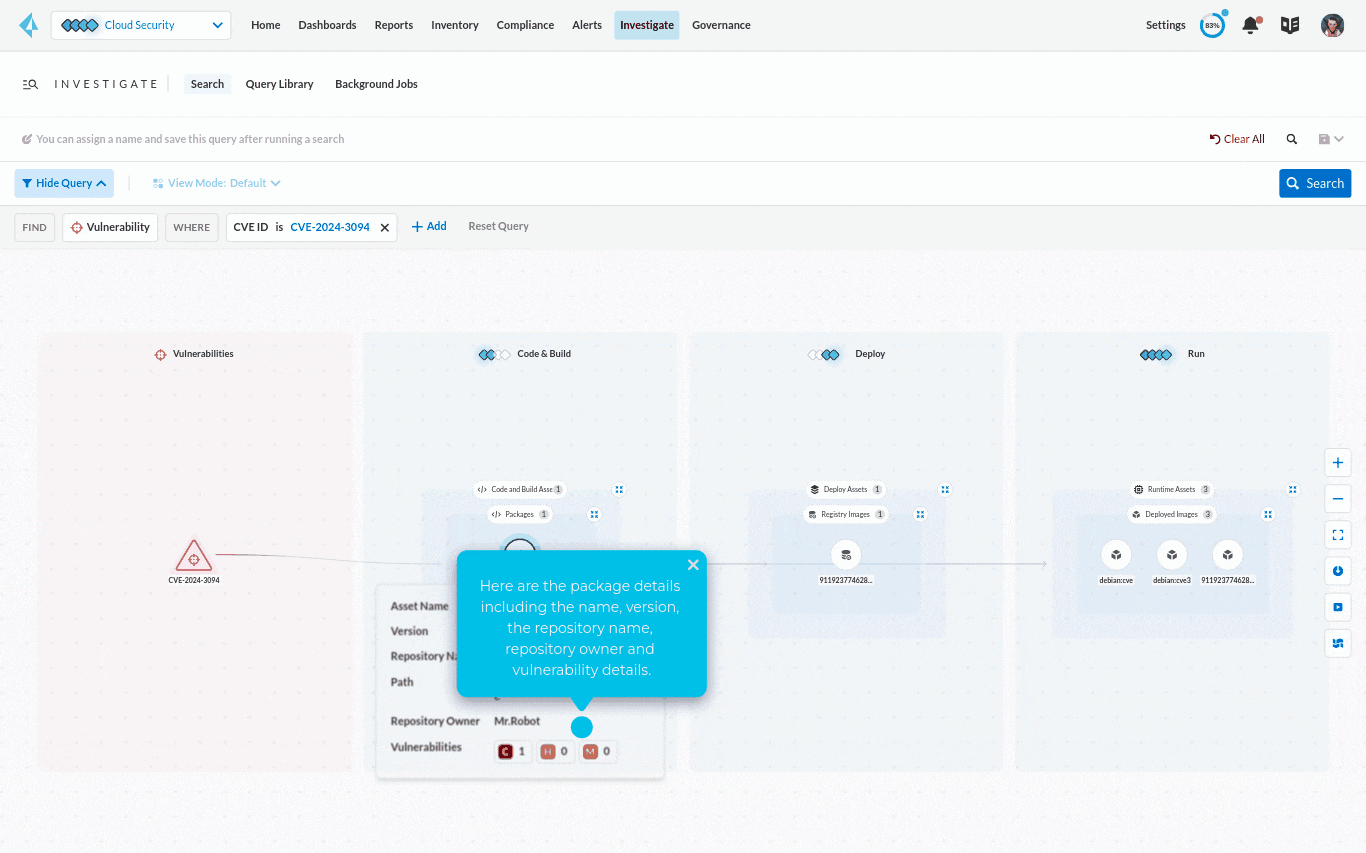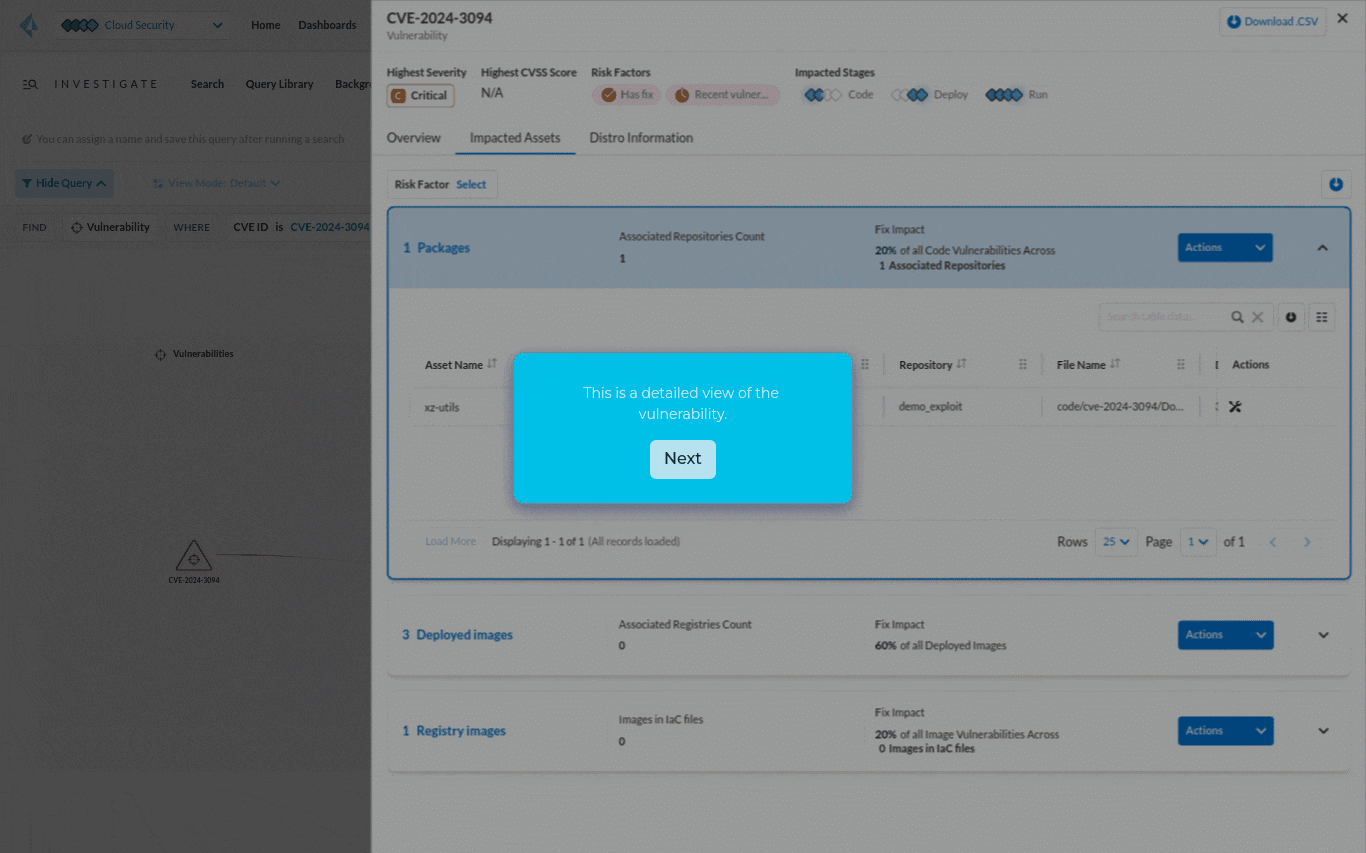
Step 2: Identify who owns the application and its content
The contextual information such as asset name, package version, repo name and owner can help pinpoint the source of the problem. By identifying who owns the application, the security team can figure out who they need to work with to fix the vulnerability.
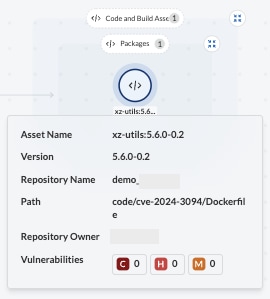
Step 3: Take action to help fix the CVE by submitting a pull request.
In the past, security teams sent emails or shared spreadsheets with developers to get them to remediate a vulnerability. Since Prisma Cloud has already figured out where the source package is, you can submit a pull request to speed up the remediation process.
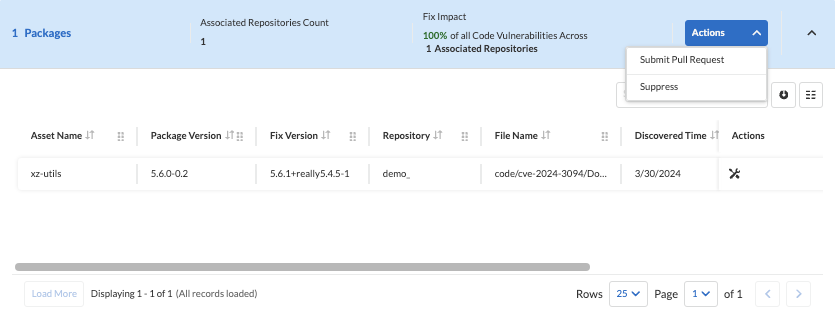
Stay Proactive with CI/CD Guardrails
Want to get ahead of your developers and stop them from deploying applications with the vulnerability? With Prisma Cloud CI/CD security capabilities, you can take proactive measures to prevent the new vulnerable workloads from being deployed. Prevent CVE-2024-3094 and other vulnerabilities from deploying into production by creating a policy that prohibits the release of new workloads with this issue (fail the build in CI) or the deployment of such workloads (block the deployment in CD).
Detect Attack Paths of Known CVEs
Prisma Cloud excels in finding and fixing vulnerabilities, as well as in visualizing potential attack vectors. It offers detailed insights into cloud-based virtual machine exposures, highlighting instances where they are publicly accessible, which increases their susceptibility to potential security breaches.
Our attack path policy, crafted specifically for this CVE, identifies cloud instances that are publicly accessible and vulnerable to CVE-2024-3094. This vulnerability could allow attackers to execute code arbitrarily, gain unauthorized control, and potentially pivot to other systems within the network. Highlighting these pathways is crucial for enabling faster response times and mitigating risks before they escalate into breaches or data loss.
Learn More
Don't just read about how Prisma Cloud can help—experience it for yourself! The UX Utils product tour is an interactive demo guiding you through steps to find and fix the CVE using Prisma Cloud. See it in action here.
Vulnerabilities are a way of life for security professionals, but that doesn’t mean they have to be the bane of your existence. By understanding the impact, creating a plan and staying proactive, you can make your own life easier in the process. Prisma Cloud’s platform approach to cloud security allows you to be the hero when it comes to managing vulnerabilities.
Put Prisma Cloud’s vulnerability management to work in your own environment—try a 30-day Prisma Cloud trial. Additionally, Cortex XDR and XSIAM customers with a Prisma Cloud integration will receive alerts from Prisma Cloud when a vulnerable version of XZ utils is identified on managed cloud assets.