As AI evolves, autonomous agents are revolutionizing industries by streamlining workflows, making real-time decisions and enhancing productivity. However, this autonomy introduces new security risks, including adversarial manipulation, unauthorized access and data poisoning.
At Palo Alto Networks, securing AI is a mission. As AI-driven ecosystems grow more sophisticated, so do their threats. We are at the forefront of AI security innovation, identifying vulnerabilities and designing resilient defenses to help protect businesses and users.
Our commitment extends beyond research—as an official sponsor of the AI Security Initiative (ASI), Palo Alto Networks is collaborating with other industry leaders to build best practices, identify critical threats and build robust security frameworks.
This collaboration between Palo Alto Networks and OWASP helps ensure that autonomous AI agents remain trustworthy and secure. The contributions of Palo Alto Networks enable businesses to deploy AI solutions confidently while safeguarding against emerging risks.
Understanding Multi-Agent AI Architecture
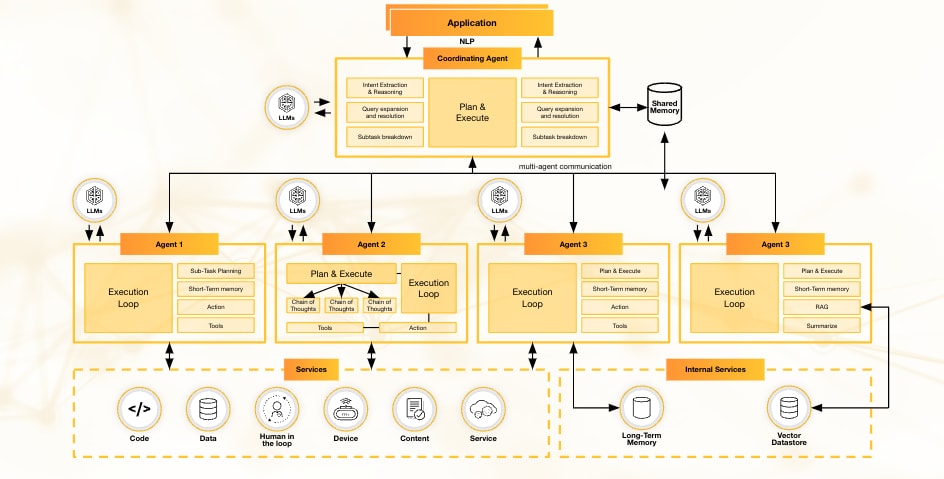
End-to-End Multi-AI Agent Architecture Workflow Diagram
Multi-AI agent architectures use a network of specialized AI agents to scale capabilities, streamline complex workflows and drive more efficient decision-making. These systems enable AI agents to communicate with one another and often include a coordinating AI agent to orchestrate tasks and ensure alignment toward business goals.
Let's understand this with a real-world example.
Imagine a travel booking autonomous multi-AI agent system that automates the entire process, allowing users to seamlessly book flights, hotels and car rentals, ensuring convenience and efficiency. This system consists of several autonomous AI agents working collaboratively, including:
- A coordinating AI agent that interprets the user’s request and compiles the final itinerary to deliver a complete travel plan.
- Specialized AI agents dedicated to handling specific tasks such as flight bookings, hotel reservations, car rentals and itinerary management.
Each AI agent autonomously interacts with external travel booking websites, databases, or APIs to retrieve relevant information and perform actions. With multiple AI agents involved in completing a singular workflow, there are multiple opportunities for malicious threat infiltration.
Palo Alto Networks Identifies 9 Top AI Agent Security Threats
Through extensive research, Palo Alto Networks has identified critical security threats targeting AI agents. These threats highlight vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to compromise data integrity, system performance and user security.
To bring these threats to life, let’s walk through how each one could play out in the travel booking example above—illustrating how such vulnerabilities can emerge in real-world, AI-powered systems.
1. Memory Poisoning
Memory poisoning is a security threat where attackers manipulate an AI agent’s memory by corrupting stored data, leading to flawed decision-making and security breaches.
Example: An attacker injects false data into a travel booking agent’s memory, causing it to book flights at no cost, leading to financial losses.
2. Tool Misuse
Tool misuse is when attackers exploit an AI agent’s capabilities by crafting deceptive prompts, causing unauthorized data access or system manipulation.
Example: A manipulated AI travel assistant retrieves sensitive customer data, cancels booked reservations without consent, or initiates unauthorized transactions.
3. Privilege Compromise
Privilege compromise happens when malicious actors exploit an AI agent’s elevated permissions to perform unauthorized actions, making unauthorized activities appear legitimate.
Example: An attacker influences an AI agent to approve fraudulent upgrades, access financial details or alter travel reservations for personal gain.
4. Resource Overload
Resource overload attacks happen when attackers flood AI agents with excessive requests, degrading system performance and accessibility.
Example: A travel reservation AI agent is overwhelmed with thousands of fake requests, slowing processing times and potentially crashing during peak hours.
5. Cascading Hallucination Attacks
Cascading hallucination attacks occur when attackers intentionally manipulate an AI agent to generate false or unreliable outputs by exploiting its tendency to make assumptions with incomplete information. This vulnerability can lead to poor decision-making and unauthorized actions, particularly dangerous in autonomous systems where the AI agent acts on fabricated information without human verification.
Example: A travel AI agent is tricked into misinforming users that a visa isn’t required for a specific destination when it actually is required.
6. Intent-Breaking and Goal Manipulation
Intent-breaking and goal manipulation attacks alter an AI agent’s decision-making process, causing it to deviate from intended objectives while appearing to function normally.
Example: A travel AI agent is influenced to prioritize specific airlines or hotels, even when they aren’t the most cost-effective or relevant to user preferences.
7. Repudiation and Untraceability
Repudiation represents a critical security vulnerability where AI agents cannot be held accountable for their actions due to inadequate logging and traceability mechanisms. This vulnerability stems from the increasingly autonomous nature of AI systems that operate with growing independence across complex technological ecosystems.
Example: A travel reservation dispute arises due to a missing flight confirmation, but poor logging prevents customer support from identifying the issue.
8. Identity Spoofing and Impersonation
Identity spoofing and impersonation attacks happen when attackers exploit AI authentication mechanisms to assume an AI agent’s identity or impersonate human users, executing harmful actions under a false identity.
Example: A hacker hijacks a travel AI assistant, making unauthorized reservations or accessing payment details while impersonating the legitimate human user.
9. AI Agent Communication Poisoning
Malicious actors intercept or corrupt communication among AI agents, disrupting decision-making and system integrity.
Example: A travel AI agent is manipulated into falsely indicating that certain hotels are fully booked or providing fake flight prices, disrupting the booking process.
Strengthening AI Security for the Future
Our collaboration with the OWASP GenAI Security Project Agentic Security Initiative is pioneering AI security research and defining best practices for securing agentic systems. By understanding and mitigating AI agent-based threats, we can build resilient AI architectures that protect users, data and businesses from evolving cyber risks.
We are focused on enhancing the security of AI agents to better address the identified, emerging threats. In addition to reinforcing these existing protections, we are also exploring innovations that will make it easier for organizations to discover, protect, and monitor threats related to AI agents.
We aim to ensure that AI agents remain secure and trustworthy as they evolve and become even more integral to enterprise operations. This proactive approach will help organizations stay ahead of new threats and ensure the continued safe deployment of AI technologies.
Sign up for a personalized demo to learn more about AI Runtime Security and how it can help protect against runtime threats.